Medicine Research: The Role of Tau Filaments and Extracellular Vesicles in Alzheimer's Disease
Understanding Tau Filaments and Their Impact
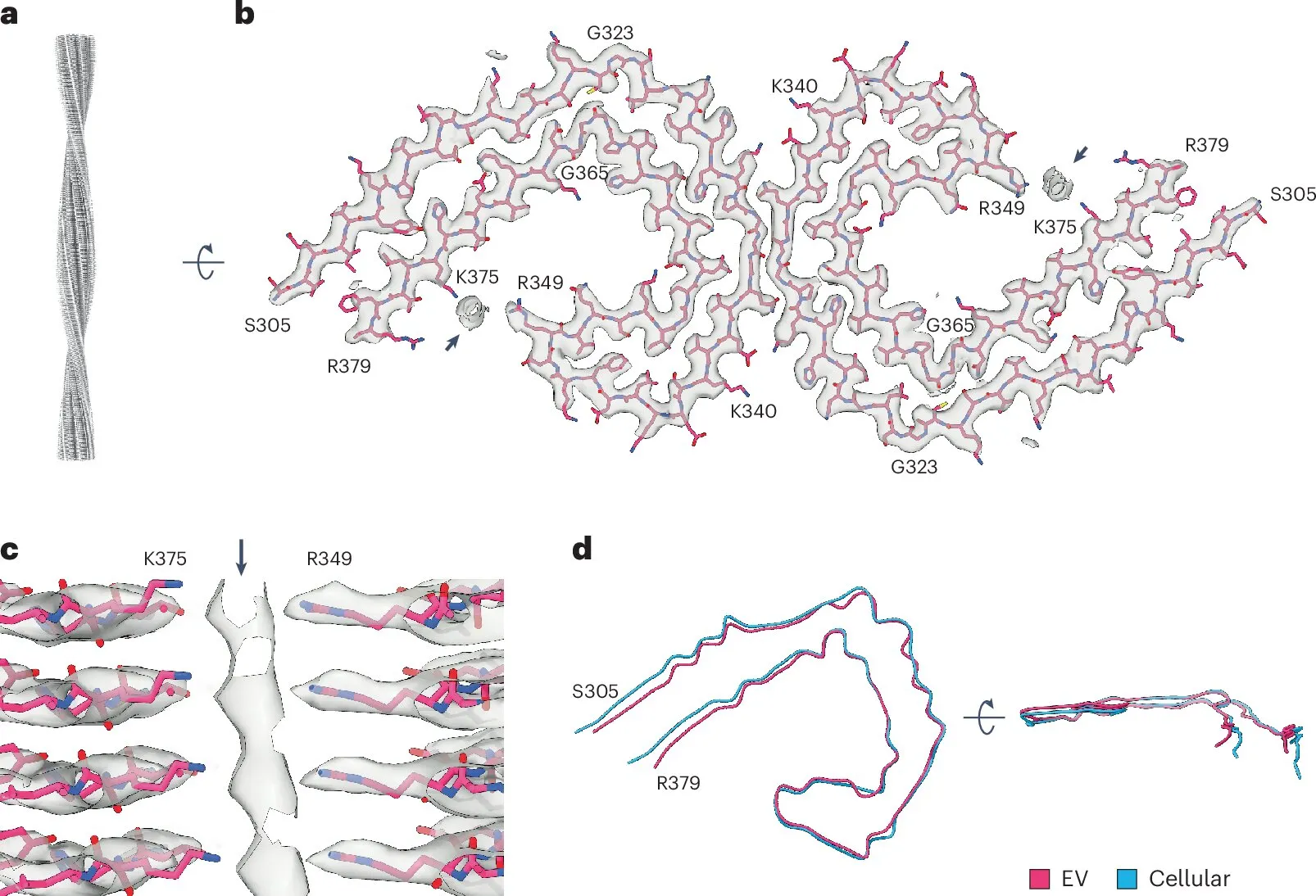
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a debilitating neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a progressive decline in memory and cognitive function. Recent medicine research highlights the connection between Tau filaments and extracellular vesicles, suggesting their significant roles in disease progression. Researchers are increasingly focusing on these components to unveil the complex pathology of Alzheimer's disease.
The Importance of Extracellular Vesicles in Health Research
- Extracellular vesicles serve as important biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of AD.
- Research indicates that Tau protein aggregation can influence vesicle formation and functionalities.
- Understanding these processes may lead to innovative therapeutic approaches in health science.
Future Directions in Medicine Science
- Further studies are needed to explore the therapeutic potential of targeting Tau filaments.
- Interdisciplinary collaborations are essential for advancing health research.
- In-depth mechanisms involving extracellular vesicles must be elucidated.
This research not only enhances knowledge but also opens doors to potentially groundbreaking interventions in Alzheimer's disease.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.