Chronic Disease Research Highlights Stalling Progress in Alcohol and Cancer Mortality Rates
Chronic Diseases: An Overview
Chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, remain leading causes of mortality globally. Recent research reveals that advancements in reducing deaths related to these diseases are stagnating, particularly in the context of alcohol-related illnesses and communicable diseases.
Analysis of Mortality Data
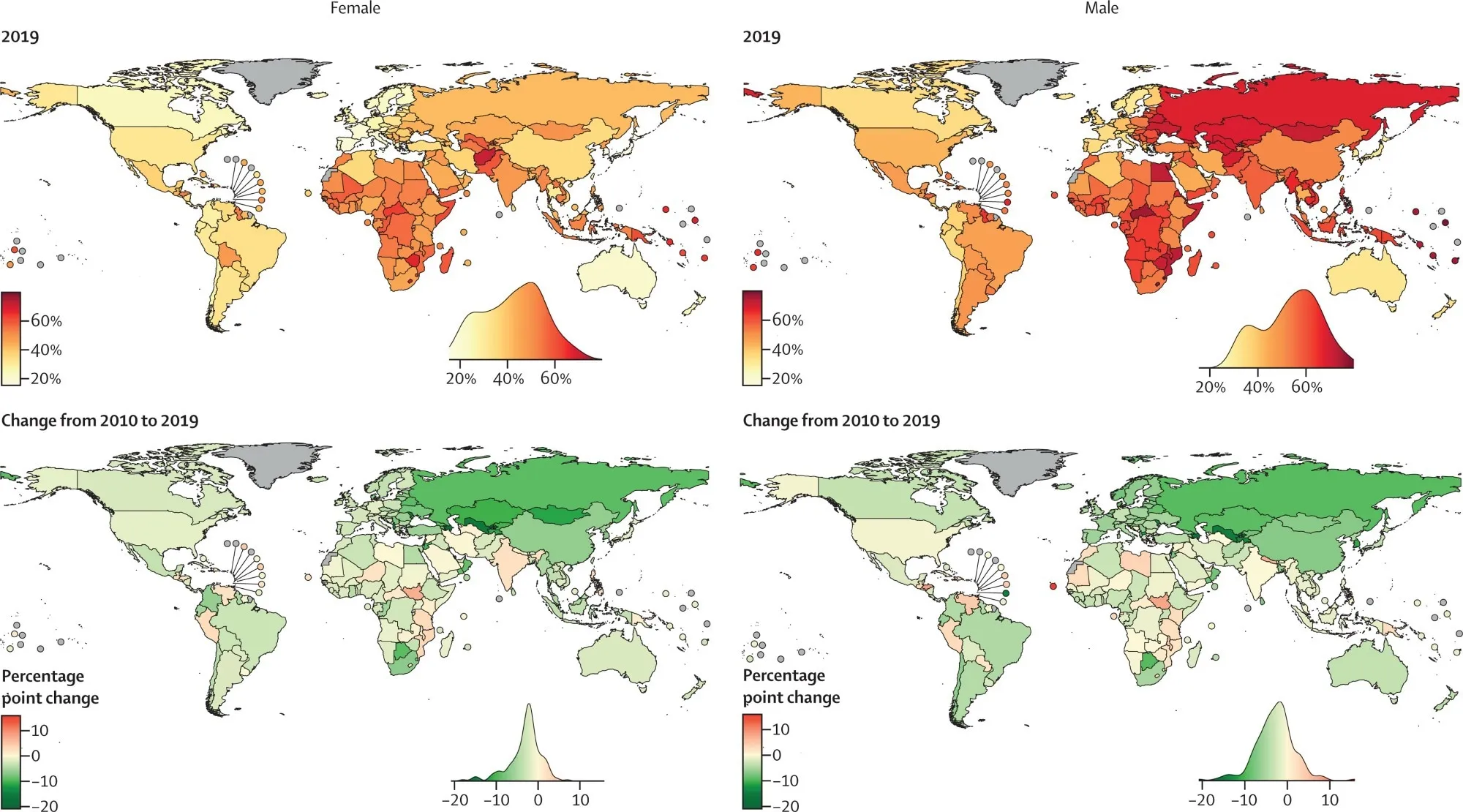
Researchers have thoroughly analyzed mortality data from 185 countries, focusing on trends in non-communicable diseases (NCDs). The findings indicate that while there was a drop in NCD deaths before age 80 from 2010 to 2019, the rate of improvement lagged when compared to the previous decade.
Key Findings
- Stalling Progress: The pace of reduction is significantly slower compared to 2001-2010.
- Alcohol and Cancer: Increases in mortality linked to liver and lung cancer complicate progress.
- Respiratory Conditions: In addition to heart disease and strokes, respiratory illnesses continue to pose significant challenges.
Implications for Public Health
This research highlights critical gaps in control and prevention strategies for chronic diseases, underscoring the need for improved health policies and interventions.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.